Examining pedagogies for teaching phonics: lessons from early childhood classrooms

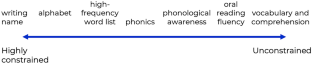
Australian early childhood education positions literacy learning as a set of social practices contextualised by one’s unique experiences and knowledges. Despite widespread agreement about the need to teach phonics and other code-breaking practices, the ways early childhood educators integrate “constrained” skills are not well understood outside the education profession. Current public discourse is generating ever-increasing pressure for the adoption of explicit teaching of phonics, however, teaching skills in isolation from reading and writing can be problematic, especially for marginalised learners. Challenges lie not only in learning to apply skills later but also in the impingement on time for more sophisticated concepts such as comprehension or vocabulary. This paper’s focus on pedagogies in early childhood educational settings prior to compulsory formal school sits within a larger project examining literacy demands for learners across school. In this paper, we argue for greater recognition of early childhood educators’ expertise in planning for and facilitating a diversity of practices that can address all learners’ needs.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve

Similar content being viewed by others
Teaching phonics in context—stories of teachers’ practice and students’ outcomes
Article Open access 10 April 2024

Feeling the pressure: Early childhood educators’ reported views about learning and teaching phonics in Australian prior-to-school settings
Article 01 February 2015
Explore related subjects
References
- Adoniou, M. (2017). Misplaced faith in synthetic phonics and the Phonics Screening Test. In M. M. Clark (Ed.), Reading the evidence: Synthetic phonics and literacy learning. (pp. 35–45). Glendale Education. Google Scholar
- Adoniou, M., Cambourne, B., & Ewing, R. (2018). What are ‘decodable readers’ and do they work? The Conversation. Retrieved November 30, 2018, from https://theconversation.com/what-are-decodable-readers-and-do-they-work-106067
- Australian Children’s Education and Care Quality Authority (ACECQA). (2012). National quality framework for early childhood education and care. Retrieved October 7, 2012, from https://www.acecqa.gov.au/national-quality-framework
- Mantei, J., & Kervin, L. (2019). What's your system? Thinking about what we mean by being ‘systematic’ in our teaching about letter-sound relationships in context. Practical Literacy: The Early and Primary Years, 24(2), 14–17.
- Mantei, J., & Kervin, L. (2020). Teacher knowledge and student learning: An examination of teacher pedagogies for the same writing topic across two consecutive grades. Australian Journal of Language and Literacy, 43(3), 224–234.
- Bizzocchi, A. L. (2017). How many phonemes does the English language have? International Journal of English Language and Literature Studies,5(10), 36–46 Google Scholar
- Bowers, J. S. (2020). Reconsidering the evidence that systematic phonics is more effective than alternative methods of reading instruction. Educational Psychology Review. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09515-yArticleGoogle Scholar
- Campbell, S. A. (2015). Feeling the pressure: Early childhood educators’ reported views about learning and teaching phonics in Australian prior-to-school settings. Australian Journal of Language and Literacy,38(1), 12–26 Google Scholar
- Campbell, S. (2020). Teaching phonics without teaching phonics: Early childhood teachers’ reported beliefs and practices. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy,20(4), 783–814 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Campbell, S., Torr, J., & Cologon, K. (2012). Ants, apples and the ABCs: The use of commercial phonics programmes in prior-to-school children’s services. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy,12(4), 367–388 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Campbell, S., Torr, J., & Cologon, K. (2014). Pre-packaging preschool literacy: What drives early childhood teachers to use commercially produced phonics programs in prior-to-school settings. Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood,15(1), 40–53 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Carter, J. (2019). Listening to the voices of children: An illuminative evaluation of the teaching of early reading in the light of the phonics screening check. Literacy,54(1), 49–57 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Castles, A., Rastle, K., & Nation, K. (2018). Ending the reading wars: Reading acquisition from novice to expert. Psychological Science in the Public Interest,19(1), 5–51 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Centre for Education Statistics & Evaluation (2017). Effective reading instruction in the early years of school: Literature Review, NSW Department of Education. Retrieved January 13, 2019, from https://www.cese.nsw.gov.au/publications-filter/literature-review-effective-reading-instruction-in-the-early-years-of-school
- Chall, J. S., Jacobs, V. A., & Baldwin, L. E. (1990). The reading crisis: Why poor children fall behind. Harvard University Press. BookGoogle Scholar
- Chambers, B., Cheung, A. C., & Slavin, R. E. (2016). Literacy and language outcomes of comprehensive and developmental-constructivist approaches to early childhood education: A systematic review. Educational Research Review,18, 88–111 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Clark, M. (2017). Reading the evidence: Synthetic phonics and literacy learning. Glendale Education. Google Scholar
- Comber, B. (2019). Educative encounters of a different kind: Pedagogies of everyday life. Curriculum Inquiry,49(2), 217–229 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Cormack, P. (2011). Reading pedagogy, “Evidence” and education policy: Learning from history? The Australian Educational Researcher,38(2), 133–148 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Davis, A. (2012). A monstrous regimen of synthetic phonics: Fantasies of research-based teaching ‘methods’ versus real teaching. Journal of Philosophy of Education,46(4), 560–573 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Department of Education Employment and Workplace Relations (DEEWR). (2009). Belonging, being and becoming: The early years learning framework for Australia. Commonwealth of Australia. Google Scholar
- Deterding, D. (2004). How many vowel sounds are there in English? STETS Language & Communication Review,19(10), 19–21 Google Scholar
- Deterding, D. (2005). How many consonant sounds are there in English? STETS Language and Communication Review,4(1), 23–25 Google Scholar
- Dockett, S., & Perry, B. (2007). Children’s transition to school: Changing expectations. In A. W. Dunlop & H. Fabian (Eds.), Informing transitions in the early years. (pp. 92–104). McGraw-Hill Education. Google Scholar
- Dougherty Stahl, K. A. (2011). Applying new visions of reading development in today’s classrooms. The Reading Teacher,65(1), 52–56 Google Scholar
- Dyson, A. H. (2019). Ethnography upside down. In N. Kucirkova, J. Rowsell, & G. Falloon (Eds.), The Routledge international handbook of learning with technology in early childhood. (pp. 74–90). Routledge. ChapterGoogle Scholar
- Ewing, R. (2018). Exploding some of the myths about learning to read: A review of research on the role of phonics. NSW Teachers Federation. Google Scholar
- Ewing, R., & Maher, M. (2014). Phonics: Its place in the literacy story. ALEA ‘Hot Topic’, October. NSW: Australian Literacy Educators’ Association. Retrieved June 6, 2019 from https://www.alea.edu.au/publicresources/alea-hot-topics
- Genishi, C. (2016). The powers of language: Toward remixing language policy, curricula, and child identities. In A. H. Dyson (Ed.), Child cultures, schooling, and literacy: Global perspectives on composing unique lives. (pp. 149–164). Routledge. Google Scholar
- Grant, S., Comber, B., Danby, S., Theobald, M., & Thorpe, K. (2018). The quality agenda: Governance and regulation of preschool teachers’ work. Cambridge Journal of Education,48(4), 515–532 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Henebery, B. (2019). New phonics plan to ‘change the future of literacy teaching’. The Educator Australia. Retrieved January 13, 2020 from https://www.theeducatoronline.com/k12/news/new-phonics-plan-to-change-the-future-of-literacy-teaching/267634
- Honan, E., Connor, J., & Snowball, D. (2017). ALEA Position Paper on the National Year 1 Phonics Check: Does Australia need an assessment tool to measure literacy and numeracy achievement in Year 1 classrooms? Practical Literacy: the Early and Primary Years,22(3), 35 Google Scholar
- Johnston, V. (2016). Successful read-alouds in today’s classroom. Kappa Delta Pi Record,52(1), 39–42 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Lonigan, C. J., Purpura, D. J., Wilson, S. B., Walker, P. M., & Clancy-Menchetti, J. (2013). Evaluating the components of an emergent literacy intervention for preschool children at risk for reading difficulties. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology,114(1), 111–130 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Loughland, T., & Thompson, G. (2016). The problem of simplification: Think-tanks, recipes, equity and ‘Turning around low-performing schools.’ The Australian Educational Researcher,43(1), 111–129 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Luke, A. (2010). Will the Australian Curriculum up the ante in primary classrooms? Professional Voice,8(1), 41–48 Google Scholar
- McArdle, F., Grieshaber, S., & Sumsion, J. (2019). Play meets early childhood teacher education. The Australian Educational Researcher,46(1), 155–175 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Moji, E. (forthcoming) Envoi: Transitions. In P. T. Jones, E. Matruglio & C. Edwards-Groves (Eds.), Transition and Continuity in School Literacy Development. London: Bloomsbury.
- National Early Literacy Panel. (2008). Developing early literacy: Report of the National Early Literacy Panel. Retrieved January 29, 2021 from https://lincs.ed.gov/publications/pdf/NELPReport09.pdf.
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, NIH, DHHS. (2010). Developing early literacy: Report of the National Early Literacy Panel. U.S. Government Printing Office. Google Scholar
- Paris, S. G. (2005). Reinterpreting the development of reading skills. Reading Research Quarterly,40(2), 184–202 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Paris, S. G., & Luo, S. W. (2010). Confounded statistical analyses hinder interpretation of the NELP report. Educational Researcher,39(4), 316–322 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Perry, B., Dockett, S., Mason, T., & Simpson, T. (2007). Successful transitions from prior-to-school to school for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander. International Journal,5, 102–111 Google Scholar
- Quinn, M. F., & Bingham, G. E. (2019). The nature and measurement of children’s early composing. Reading Research Quarterly,54(2), 213–235 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Resnick, L. B. (2010). 2009 Wallace Foundation Distinguished Lecture. Educational Researcher,39(3), 183–197 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Robinson, N. (2019). Reading wars rage again as Australian Government pushes to introduce phonics test. Australian Broadcasting Commission (ABC) Retrieved December 13, 2020 from https://www.abc.net.au/news/2019-06-30/australian-phonics-war-on-how-to-teach-kids-to-read-rages-on/11258944
- Rose, J. (2006). Independent review of the teaching of early reading. Final report. Department for Education and Skills (DfES) Publications. Google Scholar
- Smith, R. (2015). Reading Recovery program used in 960 NSW public schools does not work. Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved December 13, 2020 from https://www.smh.com.au/national/nsw/reading-recovery-program-used-in-960-nsw-public-schools-does-not-work-20151218-glqplg.html
- Snow, C. E., & Matthews, T. J. (2016). Reading and language in the early grades. The Future of Children,26(2), 57–74 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Tang, X., Kikas, E., Pakarinen, E., Lerkkanen, M. K., Muotka, J., & Nurmi, J. E. (2017). Profiles of teaching practices and reading skills at the first and third grade in Finland and Estonia. Teaching and Teacher Education,64, 150–161 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Torgerson, C., Brooks, G., & Hall, J. (2006). A systematic review of the research literature on the use of phonics in the teaching of reading and spelling. DfES Publications. Google Scholar
- Urban, R. (2018). Researchers urge phonics lessons for all preschoolers, The Australian. Retrieved December 13, 2020 from https://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/nation/researchers-urge-phonics-lessons-for-all-preschoolers/news-story/6b2d718252625c266b78c68c00f542b6
- Wyse, D., & Goswami, U. (2008). Synthetic phonics and the teaching of reading. British Educational Research Journal,34(6), 691–710 ArticleGoogle Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Faculty of the Arts, Social Sciences and Humanities, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia Jessica Mantei, Lisa Kervin & Pauline Jones
- Jessica Mantei





